Are you learning an endangered language?
We’re now into the third week of our uTalk Challenge! Over 350 people are taking part and over 40 languages have been chosen to learn! The most popular languages are some of the most spoken ones in the world like Polish, Spanish and Japanese.
Interestingly, we also have some endangered languages chosen. UNESCO publishes a list of the languages that are classed as endangered; there are five different levels, from Vulnerable (most children speak the language but only in restricted places) to Extinct (no one speaks the language anymore). Some of these surprised as me as Welsh, Scottish Gaelic and Irish are all on the UNESCO list. Hawaiian is on the list as ‘critically endangered’, which is one level away from being extinct, due to the speakers of the language being the oldest generation of the family.
When it comes to our uTalk Challenge here are the four of the endangered languages that have been chosen:
Basque
There are around 660,000 speakers left of this language and although spoken in Europe it’s not classed as the Indo-European family of languages, potentially due to it being totally unique, with no similarities to any other languages. There are many theories on where the Basque language comes from, but none of these have conclusive evidence. One of our uTalk Challengers, Patricia, is learning Basque and quickly selected ‘garagardoa’ as her favourite word for beer in any language! Find out why in her video.
Scottish Gaelic
It is quite clear that Scottish Gaelic is spoken in some parts of Scotland, mainly in the Western Isles. It is one of the three languages in Scotland, with English and Scots also being spoken. Scots is also classed as an Endangered language, but on a lower level than Scottish Gaelic. There are around 60,000 people who speak Scottish Gaelic still. However, across many Scottish schools the introduction of Scottish Gaelic began in the 1980s, with it now being taught across primary and middle schools.
Welsh
Welsh is Britain’s oldest language, dating back to around 4,000 years ago. Today there are 750,000 speakers; this is around 20% of the Welsh population. Welsh is most popular in the west of the country; however, there is evidence that more schools in Wales are now teaching the language. Within Wales there are two main dialects, North and South Walian. It is hard to establish where these two dialects cross over, as they both have different accents, vocabulary and grammar points. Liz and Nat from the EuroTalk office are learning Welsh for the challenge (in fact Nat’s already completed the app because she’s much better at languages than the rest of us!).
Wolof
This is one of the six main languages in Senegal. Originally written with an Arabic alphabet, it was then standardised using the Latin alphabet. A lot of Wolof speakers use French loan words when speaking the language, which could be one of the reasons Wolof has become an endangered language. In certain urban areas of Senegal people use a mix of Arabic, French and Wolof but in Gambia they use English words as loan words instead.
Do you speak any endangered languages? Please let us know on Twitter or our Facebook page. Or if you’d like to learn an endangered language, you can find all of the above and more in our uTalk app.
Alex
10 reasons to visit… the Outer Hebrides
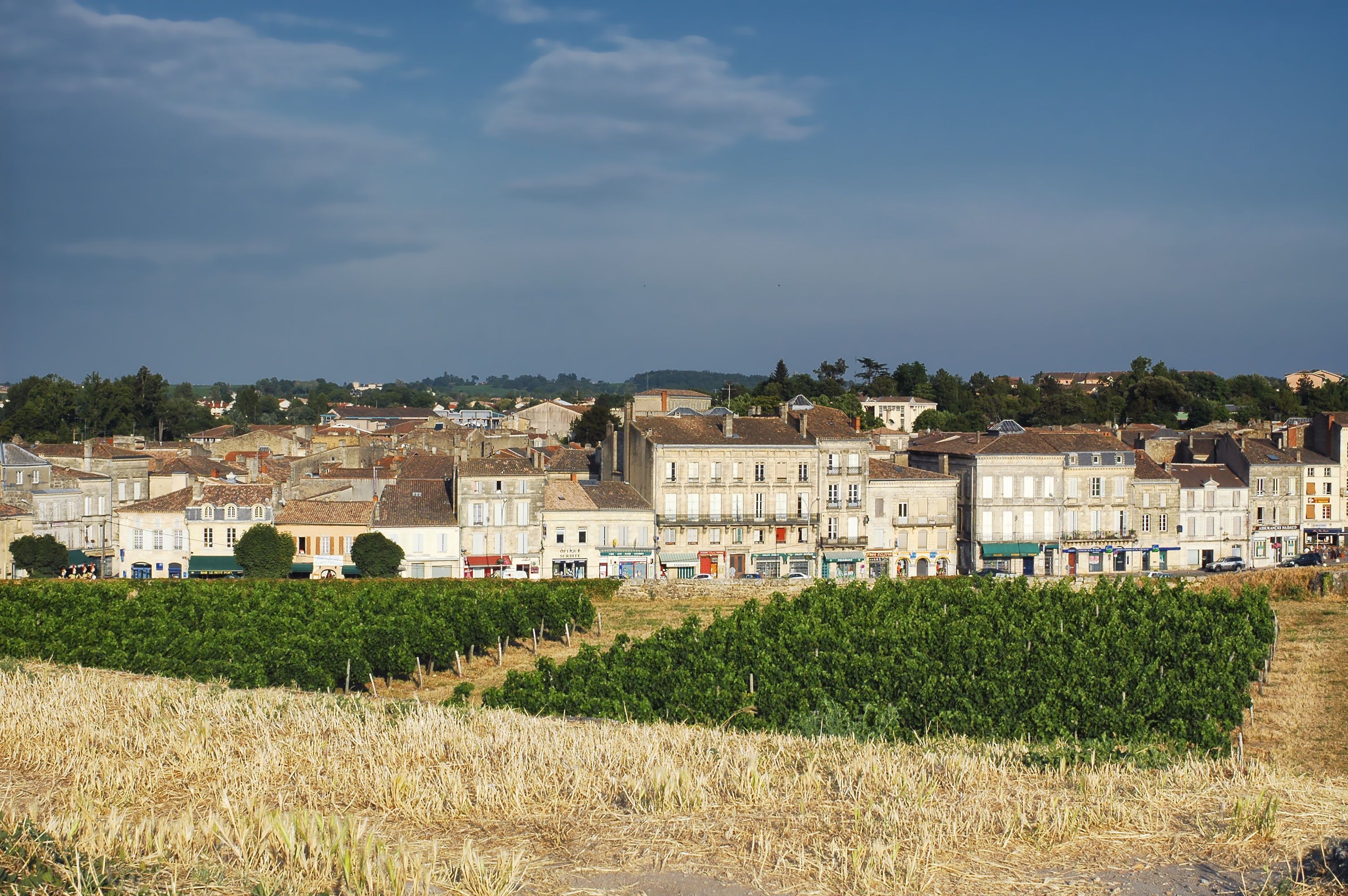
The scattered islands of the Outer Hebrides, off the Western coast of Scotland, are a haven of beauty, wildlife and mysterious archaeology. Tying in with last week’s Scottish Week here at EuroTalk, these are my top ten reasons to visit the islands, where Scottish Gaelic is still spoken as a native language.
We’d love to hear from residents or fans of this gorgeous part of the world – send us your tips!
1. The beautiful, beautiful scenery
Everybody, without exception, is blown away by the views on the Hebrides, where beaches are bright white and stretch out against a distant, uninterrupted horizon. The air is crisp and unpolluted and the seas, ever changing, create a dramatic backdrop to island life. Go driving and you might be the only person on the wide road for miles. Each of the islands has its own distinct geographical characteristics, from Lewis’ flatness to Harris’ mountains.
2. Black pudding
A local delicacy you’ll hopefully be presented with early on in your trip, Stornoway Black Pudding is now famous the world over. After a couple of slabs of it on your breakfast plate, you’ll not go hungry for the day, and if you’re feeling especially indulgent you might even round the meal off with a couple of kippers smoked in one of the island’s smokehouses. Yum!
3. Harris Tweed
Now internationally famous and found on Nike shoes, the tweed is traditionally made to protect against the extreme weather to be found on the island. It’s well worth taking a visit to one of the workshops or outlets to find out how it has been handmade by locals for centuries, up to the present day.
4. St Kilda
Admittedly, this is not a trip for the faint-hearted, as St Kilda lies a good eight hours’ travel by charter boat from the Hebrides, more from the mainland. Still, if you have time to play with, St Kilda is a fascinating trip. Its story of evacuation in the 1930s, after a period of extreme poverty and starvation, really hits home if you visit the museum, located in the homes of the original residents. The island is also a National Nature Reserve and a likely place to spot interesting flora and fauna.
5. The Blackhouse
You’ll find these in both the Highlands and Hebrides, and if you fancy you can even stay in one in the village of Gearrannan on Lewis, where the blackhouses have become visitor accommodation and you can experience for yourself the cosy, warm, smokey atmosphere. The blackhouse is a traditional home for both people (in one half) and their livestock (in the other), with the peculiar distinction that there is no chimney: instead, the smoke from the central hearth builds up and eventually filters through the thatched roof, creating a smokey, peaty and very warming atmosphere within.
6. Going to a whisky distillery
You can’t really miss this one, and generally in Scotland you’ll have a lot of local distilleries to choose from. On Lewis, you can visit the relatively new Abhainn Dearg distillery (the most westerly one in Scotland) and practice that all-important Gaelic word – Sláinte!
7. Ferries and planes
Island hopping around the Hebrides gives you the chance to see first-hand the vast differences in scenery, and character, of the many different islands. The archipelago is connected by a network of ferries, which, if you have a car, are well worth booking in advance to avoid being stranded somewhere for days. There are also a number of miniature plane journeys to be made, including the shortest ever flight, from Westray to Papa Westray, which takes a mere 1 minute 14 seconds. Don’t be alarmed if your plane only seats up to 8 people or if it lands, a little surprisingly, on the beach, as it does on Barra.
8. Rain
It’s probably a bit optimistic to expect perfect sunshine, even in the summer months, but luckily the Outer Hebrides look majestic in rain, and there is something deeply dramatic about the sudden and extreme downpour, swooping in within minutes, which can drench you to the skin. Nothing to worry about if you’re staying in the blackhouse and get to dry off in front of a peat fire, of course!
9. Wildlife
Undoubtedly this is one of the main reasons many people visit the islands. From the puffin to the golden eagle to the Minke whale, the islands, with their stunning natural beauty, are host to a rich variety of creatures which elsewhere are rarely seen.
10. Archaeology
Ranging from the very famous to the barely explored, the Hebrides are full of archaeological wonders from all ages. Perhaps the most well visited are the Callanish Stones on Lewis’ Western coast, which local legend (as often happens with standing stones) attributes to a group of naughty local giants turned to stone as punishment. Legends aside, the stones are enormous and imposing, and especially chilling if you manage to avoid the crowds and view them, early in the cold morning, huddled conspiratorially across the horizon.
Have we convinced you to give the Outer Hebrides a try? Don’t forget to learn a few words in Scottish Gaelic before you go…
Nat
Languages of the week: Scotland
This week we’re celebrating Scotland, in honour of the Braemar Gathering of the Scottish Highland Games, which took place this weekend.
 The Braemar Gathering is one of many events that make up the Highland Games from May to September each year. It’s attended by 16,000 people, including members of the Royal Family. Events include tossing the caber, putting the stone, Highland dancing and piping, and competitors must dress in Highland costumes.
The Braemar Gathering is one of many events that make up the Highland Games from May to September each year. It’s attended by 16,000 people, including members of the Royal Family. Events include tossing the caber, putting the stone, Highland dancing and piping, and competitors must dress in Highland costumes.
Scotland has three languages: Scottish Gaelic, Scots and Scottish English – all of which you can now learn with uTalk.
Scottish Gaelic
The Scottish Gaelic alphabet has 18 letters, each of which is named after a tree or shrub.
It’s spoken by 60,000 people, mainly in the Highlands and the Western Isles, but also in Glasgow, Edinburgh and Inverness.
There are also small Gaelic speaking communities in Canada, particularly in Alba Nuadh and on the Cape Breton Islands.
Scottish Gaelic was seen as a declining language, but recently there’s been a real resurgence in schools and an increased presence in the media. The BBC operates a Gaelic language radio station, Radio nan Gàidheal.
Scots
Scots is spoken in the Lowlands and Northern Isles of Scotland. It has four dialects: Insular Scots, Northern Scots, Central Scots and Southern Scots.
A Germanic language variety, Scots is influenced by Gaelic, Norse, Latin, Dutch, Norman French, Standard French and English.
The poet Robert Burns wrote in Scots; a well-known example is Auld Lang Syne, which was written in 1788 and is now traditionally sung at New Year.
So here’s your Challenge of the Week – we want to hear you singing (or reciting, if singing’s not your thing) Auld Lang Syne in the original Scots. If you’re not sure of the words, the BBC website can help. Send us your videos on Twitter to @EuroTalk with hashtag #1788Scots
Scottish English
Also known as SSE (Standard Scottish English), Scottish English dates back to the 17th century, when Scots and English combined.
Although an English speaker can understand Scottish English, the language contains a lot of different words. Some examples are: ‘poke’, which in Scottish English is a container for chips, ‘ken’, which means ‘know’, and ‘aye’, which is the Scottish way of saying ‘yes’.
A few fun facts about Scotland
The national animal of Scotland is the unicorn.
The shortest scheduled flight in the world is from Westray to Papa Westray in the Orkney Islands of Scotland. At just one and a half miles long, it only takes 1 minute 14 seconds.
Scotland’s traditional dish, haggis, consists of the heart, liver and lungs of a sheep boiled in its stomach. It’s tastier than it sounds!
The first recorded sighting of the Loch Ness Monster was in 565 AD, when a ‘water beast attacked one of St Columba’s followers in the loch’.
What’s your favourite Scotland fact?